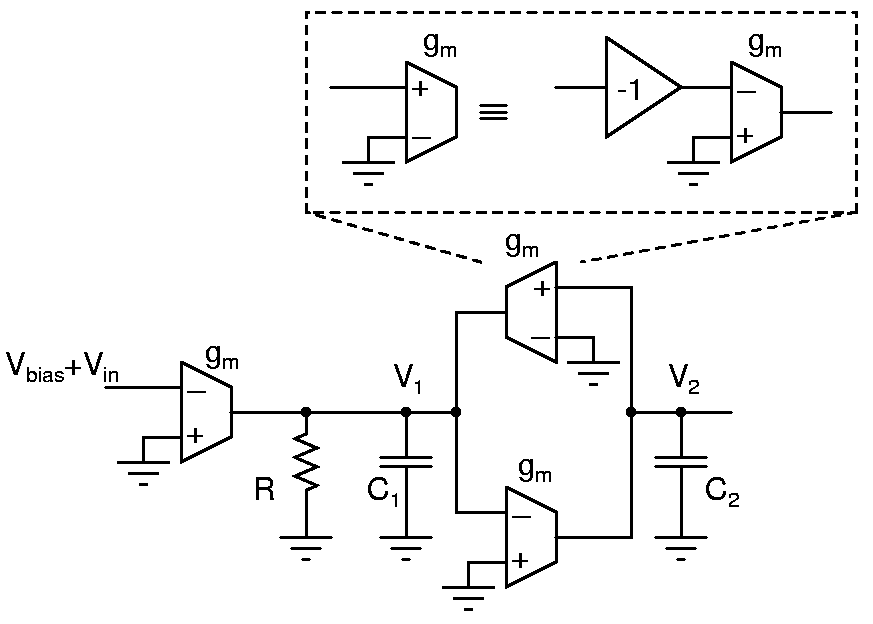
gm-C filter
A CMOS inverter biased in its active region behaves like a transconductor with its positive input grounded. Determine the impedance of an inverter whose output is shorted to its input. Measure the transconductance by forming a voltage divider with this impedance and measuring the voltages vx and vy as shown above. Do the measurements at 5V, 6V, and 7V supplies. Also note the dc bias voltage of the self biased inverter.
Design the gm-C filter shown above for a resonant frequency of 5kHz and a quality factor of 2. Determine the transfer functions between the input and V1 and V2. Build the filter using only transconductors and capacitors. i.e. the resistor and the positive transconductor should be realized using only the inverters available on a 4069.
Measure the circuit and verify that it realizes the transfer functions given above. Filters can be measured by injecting sinusoidal inputs and observing inputs and outputs on 2 channels of an oscilloscope. Also, the phase difference between input and output can be gauged from X-Y plots, and the center frequency determined. Observe the step response by injecting a low frequency square wave to the filter.
Tune the filter using the power supply voltage and verify that it tunes as expected. The voltage Vbias in the input should be the bias of the self biased inverter.